How Adaptive IP enables ever-demanding mobile video viewership
There is an explosion in bandwidth demand in India, driven by heightened user expectations as they become increasingly mobile and want the ability to consume high-definition content, video, and applications when and where they choose. Consider these statistics:
- India's online video market is expected to grow from $700 million in 2018 to $2.4 billion by 2023, according to Media Partners Asia.
- Views of videos 30 minutes or longer doubled in two years as a percentage of total viewing in India. This compounds network pressure to maintain video streaming quality for the end user.
- 65% of Indian viewers use mobile data networks to view content, higher than the 51% in developed markets, according to Vuclip.
This confluence results in a need to adapt network architectures to reduce latency, with a robust edge tied to India’s data center buildouts.
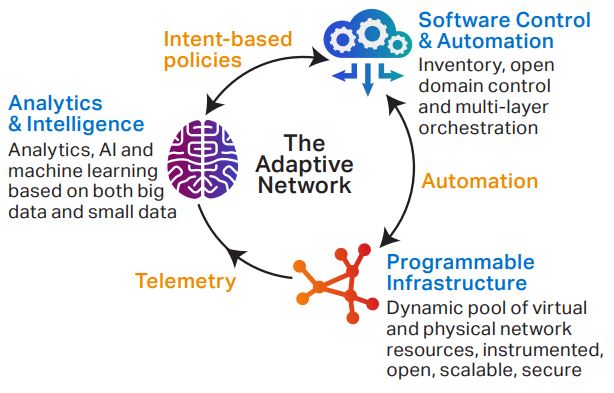
Ciena has comprehensively visualized architectural needs as the Adaptive Network™. In translating this to rolling out new Ciena solutions, we began by challenging and addressing the traditional Layer 0 network mindset with Liquid Spectrum. We’re now challenging traditional IP network thinking via Adaptive IP™.
Why approach IP differently
As networks continue to scale, the amount of data collected coupled with a never-ending need for more bandwidth mandate a need to evolve. IP technology is the industry choice for emerging applications, and the way IP protocols are delivered must evolve. It no longer makes sense to continue deploying large, complex, multi-purpose “god boxes” due to new and emerging use cases. The new mindset leverages cloud-like scale and disaggregation.
Operators need to evolve the network to be more adaptive and efficient, allowing for rapid service creation, deployment, and modification that maintains pace with user demands. What is obvious is that IP-based solutions built upon a node level control plane approach are no longer the best path forward.
The entire end-to-end network must be agile to enable compute, storage and networking resources when and where required by leveraging programmable resources that don’t require physical reconfiguration to accommodate evolving service demands. A new way of scaling and simplifying IP-based access to metro networks is required – one that is streamlined, virtualized, automated, and far more scalable. We call this new approach Adaptive IP ™.
How Adaptive IP works
Adaptive IP embraces an SDN-oriented future of networking, which provides a bridge for existing IP networks to meet future network architecture needs. This Ciena approach goes beyond the individual capabilities of a network element and builds upon programmable network infrastructure. Our intelligent automation implementation combines SDN-based orchestration with analytics. This allows operators to leverage deep network knowledge to power the automation of services and operations.
Network elements include functionality to detect and report network status by acting as sensors at points along the end-to-end service chain. This information is shared with network management and analytics applications. Based on ongoing analysis of collected data, adjustments are continually made to optimize performance of the end-to-end network. Adjustments are sent to network elements via standardized technologies, such as using NETCONF/YANG and routing protocol extensions. This forms a closed-loop systematic approach.
Adaptive IP is a Layer 3-oriented network architecture that does not start with the capabilities of a single box or collection or boxes. Instead, the design starts with a holistic, end-to-end mindset. Given the goal to be more scalable via an increased number of endpoints, there’s a desire to significantly reduce node-based control plane level signaling. In current IP/MPLS networks, each node runs a Label Distribution Protocol (LDP) to each peer router.
Adaptive IP embraces a simpler approach aligned the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)’s emerging concepts, around reducing the network’s legacy protocols and control plane signaling. The aim is to reduce which protocols to use in the programmable network infrastructure yet still support Layer 2 and Layer 3 services. For example, Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) has been enhanced with extensions to fit this need, while other protocols, such has RIP (Routing Information Protocol), have be pushed aside.
Leveraging openness
By following open standards, Ciena empowers operators to pick and choose when and where to evolve their network infrastructure and services. Solutions are no longer tightly integrated proprietary systems; rather, they’re a modular, disaggregated set of functions that can be physical and/or virtual utilizing standardized protocols to interact with one another in a microservices-based architecture.
Solving for now while preparing for the future
Strengthening the edge while maintaining cost efficiency and flexibility is a network architecture necessity. With Adaptive IP, India’s operators can solve contemporary pressures like those coming from skyrocketing mobile video, while also preparing for the era of 5G, IoT, and related applications such as smart cities, all of which will drive more demanding and mobile traffic.
To learn more about how to modernize your network, check out Ciena’s products and resources on Packet Networking.










